In February 2016, Rotten Tomatoes — the site that aggregates movie and TV critics’ opinions and tabulates a score that’s “fresh” or “rotten” — took on an elevated level of importance. That’s when Rotten Tomatoes (along with its parent company Flixster) was acquired by Fandango, the website that sells advance movie tickets for many major cinema chains.
People had been using Rotten Tomatoes to find movie reviews since it launched in 2000, but after Fandango acquired the site, it began posting “Tomatometer” scores next to movie ticket listings. Since then, studio execs have started to feel as if Rotten Tomatoes matters more than it used to — and in some cases, they’ve rejiggered their marketing strategies accordingly.
It’s easy to see why anyone might assume that Rotten Tomatoes scores became more tightly linked to ticket sales, with potential audiences more likely to buy tickets for a movie with a higher score, and by extension, giving critics more power over the purchase of a ticket.
But that’s not the whole story. And as most movie critics (including myself) will tell you, the correlation between Rotten Tomatoes scores, critical opinion, marketing tactics, and actual box office returns is complicated. It’s not a simple cause-and-effect situation.
My own work is included in both Rotten Tomatoes’ score and that of its more exclusive cousin, Metacritic. So I, along with many other critics, think often of the upsides and pitfalls of aggregating critical opinion and its effect on which movies people see. But for the casual moviegoer, how review aggregators work, what they measure, and how they affect ticket sales can be mysterious.
So when I got curious about how people perceive Rotten Tomatoes and its effect on ticket sales, I did what any self-respecting film critic does: I informally polled my Twitter followers to see what they wanted to know.
Here are seven questions that many people have about Rotten Tomatoes, and review aggregation more generally — and some facts to clear up the confusion.
How is a Rotten Tomatoes score calculated?
The score that Rotten Tomatoes assigns to a film corresponds to the percentage of critics who’ve judged the film to be “fresh,” meaning their opinion of it is more positive than negative. The idea is to quickly offer moviegoers a sense of critical consensus.
“Our goal is to serve fans by giving them useful tools and one-stop access to critic reviews, user ratings, and entertainment news to help with their entertainment viewing decisions,” Jeff Voris, a vice president at Rotten Tomatoes, told me in an email.
The opinions of about 3,000 critics — a.k.a. the “Approved Tomatometer Critics” who have met a series of criteria set by Rotten Tomatoes — are included in the site’s scores, though not every critic reviews every film, so any given score is more typically derived from a few hundred critics, or even less. The scores don’t include just anyone who calls themselves a critic or has a movie blog; Rotten Tomatoes only aggregates critics who have been regularly publishing movie reviews with a reasonably widely read outlet for at least two years, and those critics must be “active,” meaning they’ve published at least one review in the last year. The site also deems a subset of critics to be “top critics” and calculates a separate score that only includes them.
Some critics (or staffers at their publications) upload their own reviews, choose their own pull quotes, and designate their review as “fresh” or “rotten.” Other critics (including myself) have their reviews uploaded, pull-quoted, and tagged as fresh or rotten by the Rotten Tomatoes staff. In the second case, if the staff isn’t sure whether to tag a review as fresh or rotten, they reach out to the critic for clarification. And critics who don’t agree with the site’s designation can request that it be changed.
As the reviews of a given film accumulate, the Rotten Tomatoes score measures the percentage that are more positive than negative, and assigns an overall fresh or rotten rating to the movie. Scores of over 60 percent are considered fresh, and scores of 59 percent and under are rotten. To earn the coveted “designated fresh” seal, a film needs at least 40 reviews, 75 percent of which are fresh, and five of which are from “top” critics.
What does a Rotten Tomatoes score really mean?
A Rotten Tomatoes score represents the percentage of critics who felt mildly to wildly positively about a given film.
If I give a film a mixed review that’s generally positive (which, in Vox’s rating system, could range from a positive-skewing 3 to the rare totally enamored 5), that review receives the same weight as an all-out rave from another critic. (When I give a movie a 2.5, I consider that to be a neutral score; by Rotten Tomatoes’ reckoning, it’s rotten.) Theoretically, a 100 percent Rotten Tomatoes rating could be made up entirely of middling-to-positive reviews. And if half of the critics the site aggregates only sort of like a movie, and the other half sort of dislike it, the film will hover around 50 percent (which is considered “rotten” by the site).
Contrary to some people’s perceptions, Rotten Tomatoes itself maintains no opinion about a film. What Rotten Tomatoes tries to gauge is critical consensus.
Related
Why people are freaking out over Wonder Woman’s stellar Rotten Tomatoes score
Critics’ opinions do tend to cluster on most films. But there are always outliers, whether from contrarians (who sometimes seem to figure out what people will say and then take the opposite opinion), or from those who seem to love every film. And critics, like everyone, have various life experiences, aesthetic preferences, and points of view that lead them to have differing opinions on movies.
So in many (if not most) cases, a film’s Rotten Tomatoes score may not correspond to any one critic’s view. It’s more like an imprecise estimate of what would happen if you mashed together every Tomatometer critic and had the resulting super-critic flash a thumbs-up or thumbs-down.
Rotten Tomatoes also lets audiences rate movies, and the score is often out of step with the critical score. Sometimes, the difference is extremely significant, a fact that’s noticeable because the site lists the two scores side by side.
There’s a straightforward reason the two rarely match, though: The critical score is more controlled and methodical.
Why? Most professional critics have to see and review many films, whether or not they’re inclined to like the movie. (Also, most critics don’t pay to see films, because studios hold special early screenings for them ahead of the release date, which removes the decision of whether they’re interested enough in a film to spend their hard-earned money on seeing it.)
But with Rotten Tomatoes’ audience score, the situation is different. Anyone on the internet can contribute — not just those who actually saw the film. As a result, a film’s Rotten Tomatoes score can be gamed by internet trolls seeking to sink it simply because they find its concept offensive. A concerted effort can drive down the film’s audience score before it even comes out, as was the case with last year’s all-female reboot of Ghostbusters.
Even if Rotten Tomatoes required people to pass a quiz on the movie before they rated it, the score would still be somewhat unreliable. Why? Because ordinary audiences are more inclined to buy tickets to movies they’re predisposed to like — who wants to spend $12 to $20 on a film they’re pretty sure they’ll hate?
So audience scores at Rotten Tomatoes (and other audience-driven scores, like the ones at IMDb) naturally skew very positive, or sometimes very negative if there’s any sort of smear campaign in play. There’s nothing inherently wrong with that. But audience scores tend to not account for those who would never buy a ticket to the movie in the first place.
In contrast, since critics see lots of movies — some of which they would have gone to see anyhow, and some of which they would’ve never chosen to see if their editors didn’t make the assignment — their opinion distribution should theoretically be more even, and thus the critical Rotten Tomatoes score more “accurate.”
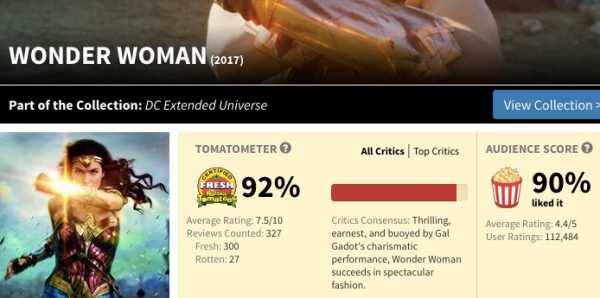
Or at least that’s what Rotten Tomatoes thinks. The site displays a movie’s critics’ scores — the official Tomatometer — at Fandango and in a more prominent spot on the movie’s Rotten Tomatoes landing page. The audience score is also displayed on the Rotten Tomatoes page, but it’s not factored into the film’s fresh or rotten rating, and doesn’t contribute to a film being labeled as “certified fresh.”
Why do critics often get frustrated by the Tomatometer?
The biggest reason many critics find Rotten Tomatoes frustrating is that most people’s opinions about movies can’t be boiled down to a simple thumbs up or down. And most critics feel that Rotten Tomatoes, in particular, oversimplifies criticism, to the detriment of critics, the audience, and the movies themselves.
In some cases, a film really is almost universally considered to be excellent, or to be a complete catastrophe. But critics usually come away from a movie with a mixed view. Some things work, and others don’t. The actors are great, but the screenplay is lacking. The filmmaking is subpar, but the story is imaginative. Some critics use a four- or five-star rating, sometimes with half-stars included, to help quantify mixed opinions as mostly negative or mostly positive.
The important point here is that no critic who takes their job seriously is going to have a simple yes-or-no system for most movies. Critics watch a film, think about it, and write a review that doesn’t just judge the movie but analyzes, contextualizes, and ruminates over it. The fear among many critics (including myself) is that people who rely largely on Rotten Tomatoes aren’t interested in the nuances of a film, and aren’t particularly interested in reading criticism, either.
But maybe the bigger reason critics are worried about the influence of review aggregators is that they seem to imply there’s a “right” way to evaluate a movie, based on most people’s opinions. We worry that audience members who have different reactions will feel as if their opinion is somehow wrong, rather than seeing the diversity of opinions as an invitation to read and understand how and why people react to art differently.
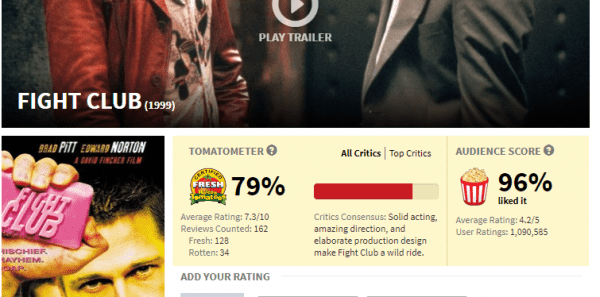
Plenty of movies — from Psycho to Fight Club to Alien — would have earned a rotten rating from Rotten Tomatoes upon their original release, only to be reconsidered and deemed classics years later as tastes, preferences, and ideas about films changed. Sometimes being an outlier can just mean you’re forward-thinking.
Voris, the Rotten Tomatoes vice president, told me that the site is always trying to grapple with this quandary. “The Rotten Tomatoes curation team is constantly adding and updating reviews for films — both past and present,” he told me. “If there’s a review available from an approved critic or outlet, it will be added.”
What critics are worried about is a tendency toward groupthink, and toward scapegoating people who deviate from the “accepted” analysis. You can easily see this in the hordes of fans that sometimes come after a critic who dares to “ruin” a film’s perfect score. But critics (at least serious ones) don’t write their reviews to fit the Tomatometer, nor are they out to “get” DC Comics movies or religious movies or political movies or any other movies. Critics love movies and want them to be good, and we try to be honest when we see one that we don’t measures up.
That doesn’t mean the audience can’t like a movie with a rotten rating, or hate a movie with a fresh rating. It’s no insult to critics when audience opinion diverges. In fact, it makes talking and thinking about movies more interesting.
If critics are ambivalent about Rotten Tomatoes scores, why do moviegoers use the scores to decide whether to see a movie?
Mainly, it’s easy. You’re buying movie tickets on Fandango, or you’re trying to figure out what to watch on Netflix, so you check the Rotten Tomatoes score to decide. It’s simple. That’s the point.
And that’s not a bad thing. It’s helpful to get a quick sense of critical consensus, even if it’s somewhat imprecise. Many people use Rotten Tomatoes to get a rough idea of whether critics generally liked a film.
The flip side, though, is that some people, whether they’re critics or audience members, will inevitably have opinions that don’t track with the Rotten Tomatoes score at all. Just because an individual’s opinion is out of step with the Tomatometer doesn’t mean the person is “wrong” — it just means they’re an outlier.
And that, frankly, is what makes art, entertainment, and the world at large interesting: Not everyone has the same opinion about everything, because people are not exact replicas of one another. Most critics love arguing about movies, because they often find that disagreeing with their colleagues is what makes their job fun. It’s fine to disagree with others about a movie, and it doesn’t mean you’re “wrong.”
(For what it’s worth, another review aggregation site, Metacritic, maintains an even smaller and more exclusive group of critics than Rotten Tomatoes — its aggregated scores cap out around 50 reviews per movie, instead of the hundreds that can make up a Tomatometer score. Metacritic’s score for a film is different from Rotten Tomatoes’ insofar as each individual review is assigned a rating on a scale of 100 and the overall Metacritic score is a weighted average, the mechanics of which Metacritic absolutely refuses to divulge. But because the site’s ratings are even more carefully controlled to include only experienced professional critics — and because the reviews it aggregates are given a higher level of granularity, and presumably weighted by the perceived influence of the critic’s publication — most critics consider Metacritic a better gauge of critical opinion.)
Does a movie’s Rotten Tomatoes score affect its box office earnings?
The short version: It can, but not necessarily in the ways you might think.
A good Rotten Tomatoes score indicates strong critical consensus, and that can be good for smaller films in particular. It’s common for distributors to roll out such films slowly, opening them in a few key cities (usually New York and Los Angeles, and maybe a few others) to generate good buzz — not just from critics, but also on social media and through word of mouth. The result, they hope, is increased interest and ticket sales when the movie opens in other cities.
Get Out, for example, certainly profited from the 99 percent “fresh” score it’s earned since its limited opening. And the more recent The Big Sick became one of the summer’s most beloved films, helped along by its 98 percent rating. But a bad score for a small film can help ensure that it will close quickly, or play in fewer cities overall. Its potential box office earnings, in turn, will inevitably take a hit.

Yet when it comes to blockbusters, franchises, and other big studio films (which usually open in many cities at once), it’s much less clear how much a film’s Rotten Tomatoes score affects its box office tally. A good Rotten Tomatoes score, for example, doesn’t necessarily guarantee a film will be a hit. Atomic Blonde is “guaranteed fresh,” with a 77 percent rating, but it hasn’t done very well at the box office despite being an action film starring Charlize Theron.
Still, studios certainly seem to believe the score makes a difference. This summer, studios blamed Rotten Tomatoes scores (and by extension, critics) when poorly reviewed movies like Pirates of the Caribbean: Dead Men Tell No Tales, Baywatch, and The Mummy performed below expectations at the box office.
2017’s 20 highest-earning movies in the US (January through August)
| Movie | US box office gross | Rotten Tomatoes | Metacritic | Vox (out of 5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Movie | US box office gross | Rotten Tomatoes | Metacritic | Vox (out of 5) |
| Beauty and the Beast | $504,014,165 | 70 | 65 | 3 |
| Wonder Woman | $409,499,021 | 92 | 76 | 3.5 |
| Guardians of the Galaxy Vol. 2 | $389,678,205 | 82 | 67 | 4 |
| Spider-Man: Homecoming | $325,116,546 | 92 | 73 | 4.5 |
| Despicable Me 3 | $258,843,180 | 61 | 49 | 2.5 |
| Logan | $226,277,068 | 93 | 77 | 4.5 |
| The Fate of the Furious | $225,764,765 | 66 | 56 | 3.5 |
| Dunkirk | $180,254,545 | 93 | 94 | 4.5 |
| The LEGO Batman Movie | $175,750,384 | 90 | 75 | 4 |
| Get Out | $175,484,140 | 99 | 84 | 4.5 |
| The Boss Baby | $174,952,304 | 51 | 50 | 2 |
| Pirates of the Caribbean: Dead Men Tell No Tales | $172,333,066 | 29 | 39 | 2 |
| Kong: Skull Island | $168,052,812 | 76 | 62 | 2.5 |
| Cars 3 | $151,484,869 | 68 | 59 | 3 |
| War for the Planet of the Apes | $144,654,763 | 93 | 82 | 4.5 |
| Split | $138,141,585 | 74 | 62 | 3 |
| Transformers: The Last Knight | $130,168,683 | 15 | 28 | 2 |
| Fifty Shades Darker | $114,434,010 | 10 | 33 | 2 |
| Girls Trip | $112,072,500 | 88 | 71 | 4 |
| Baby Driver | $105,930,256 | 94 | 86 | 4.5 |
But that correlation doesn’t really hold up. The Emoji Movie, for example, was critically panned, garnering an abysmal 6 percent Rotten Tomatoes score. But it still opened to $25 million in the US, which put it just behind the acclaimed Christopher Nolan film Dunkirk. And the more you think about it, the less surprising it is that plenty of people bought tickets to The Emoji Movie in spite of its bad press: It’s an animated movie aimed at children that faced virtually no theatrical competition, and it opened during the summer, when kids are out of school. Great reviews might have inflated its numbers, but almost universally negative ones didn’t seem to hurt it much.
It’s also worth noting that many films with low Rotten Tomatoes scores that also perform poorly in the US (like The Mummy or The Great Wall) do just fine overseas, particularly in China. The Mummy gave Tom Cruise his biggest global opening ever. If there is a Rotten Tomatoes effect, it seems to only extend to the American market.
Without any consistent proof, why do people still maintain that a bad Rotten Tomatoes score actively hurts a movie at the box office?
While it’s clear that a film’s Rotten Tomatoes score and box office earnings aren’t correlated as strongly as movie studios might like you to think, blaming bad ticket sales on critics is low-hanging fruit.
Plenty of people would like you to believe that the weak link between box office earnings and critical opinion proves that critics are at fault for not liking the film, and that audiences are a better gauge of its quality. Dwayne “The Rock” Johnson, co-star of Baywatch, certainly took that position when reviews of Baywatch came out:
Baywatch ended up with a very comfortably rotten 19 percent Tomatometer score, compared to a just barely fresh 62 percent audience score. But with apologies to The Rock, who I’m sure is a very nice man, critics aren’t weather forecasters or pundits, and they’re not particularly interested in predicting how audiences will respond to a movie. (We are also a rather reserved and nerdy bunch, not regularly armed with venom and knives.) Critics show up where they’re told to show up and watch a film, then go home and evaluate it to the best of their abilities.
The obvious rejoinder, at least from a critic’s point of view, is that if Baywatch was a better movie, there wouldn’t be such a disconnect. But somehow, I suspect that younger ticket buyers — an all-important demographic — lacked nostalgia for 25-year-old lifeguard TV show, and thus weren’t so sure about seeing Baywatch in the first place. Likewise, I doubt that a majority of Americans were ever going to be terribly interested in the fifth installment of the Pirates of the Caribbean franchise (which notched a 30 percent Tomatometer score and a 64 percent audience score), especially when they could just watch some other movie.
A pile-up of raves for either of these films might have resulted in stronger sales, because people could have been surprised to learn that a film they didn’t think they were interested in was actually great. But with lackluster reviews, the average moviegoer just had no reason to give them a chance.
Big studio publicists, however, are paid to convince people to see their films, not to candidly discuss the quality of the films themselves. So when a film with bad reviews flops at the box office, it’s not shocking that studios are quick to suggest that critics killed it.
How do movie studios try to blunt the perceived impact when they’re expecting a bad Rotten Tomatoes score?
Of late, some studios — prompted by the idea that critics can kill a film’s buzz before it even comes out — have taken to “fighting back” when they’re expecting a rotten Tomatometer score.
Their biggest strategy isn’t super obvious to the average moviegoer, but very clear to critics. When a studio suspects it has a lemon on its hands, it typically hosts the press screening only a day or two ahead of the film’s release, and then sets a review “embargo” that lifts a few hours before the film hits theaters.
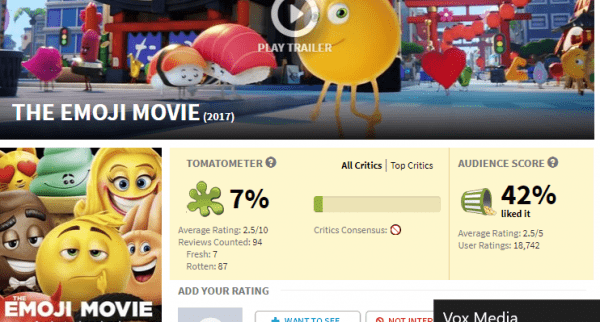
Consider, for example, the case of the aforementioned Emoji Movie. I and most other critics hoped the movie would be good, as is the case with all movies see. But once the screening invitations arrived in our inboxes, we pretty much knew, with a sinking feeling, that it wouldn’t be. The tell was pretty straightforward: The film’s only critics’ screening in New York was scheduled for the day before it opened. It screened for press on Wednesday night at 5 pm, and then the review embargo lifted at 3 pm the next day — mere hours before the first public showtimes.
Late critics’ screenings for any given film mean that reviews of the film will necessarily come out very close to its release, and as a result, people purchasing advance tickets might buy them before there are any reviews or Tomatometer score to speak of. Thus, in spite of there being no strong correlation between negative reviews and a low box office, its first-weekend box returns might be less susceptible to any potential harm as a result of bad press. (Such close timing can also backfire; critics liked this summer’s Captain Underpants, for example, but the film was screened too late for the positive reviews to measurably boost its opening box office.)
That first-weekend number is important, because if a movie is the top performer at the box office (or if it simply exceeds expectations, like Dunkirk and Wonder Woman did this summer), its success can function as good advertising for the film, which means its second weekend sales may also be stronger. And that matters, particularly when it means a movie is outperforming its expectations, because it can actually shift the way industry executives think about what kinds of movies people want to watch. Studios do keep an eye on critics’ opinions, but they’re much more interested in ticket sales — which makes it easy to see why they don’t want risk having their opening weekend box office affected by bad reviews, whether there’s a proven correlation or not.
The downside of this strategy, however, is that it encourages critics to instinctively gauge a studio’s level of confidence in a film based on when the press screening takes place. 20th Century Fox, for instance, screened War for the Planet of the Apes weeks ahead of its theatrical release, and lifted the review embargo with plenty of time to spare before the movie came out. The implication was that Fox believed the movie would be a critical success, and indeed, it was — the movie has a 97 percent Tomatometer score and an 86 percent audience score.
And still, late press screenings fail to account for the fact that, while a low Rotten Tomatoes score doesn’t necessarily hurt a film’s total returns, aggregate review scores in general do have a distinct effect on second-weekend sales. Last year, Metacritic conducted a study of the correlation between its scores and second weekend sales, and found — not surprisingly — that well-reviewed movies dip much less in the second weekend than poorly reviewed movies. This is particularly true of movies with a strong built-in fan base, like Batman v Superman: Dawn of Justice, which enjoyed inflated box office returns in the first weekend because fans came out to see it, but dropped sharply in its second weekend, at least partly due to extremely negative press.
Most critics who are serious about their work make a good-faith effort to approach each film they see with as few expectations as possible. But it’s hard to have much hope about a movie when it seems obvious that a studio is trying to play keep-away with it. And the more studios try to game the system by withholding their films from critics, the less critics are inclined to enter a screening devoid of expectations, however subconscious.
If you ask critics what studios ought to do to minimize the potential impact of a low Rotten Tomatoes score, their answer is simple: Make better movies. But of course, it’s not that easy; some movies with bad scores do well, while some with good scores still flop. Hiding a film from critics might artificially inflate first-weekend box office returns, but plenty of people are going to go see a franchise film, or a superhero movie, or a family movie, no matter what critics say.
The truth is that neither Rotten Tomatoes nor the critics whose evaluations make up its scores are really at fault here, and it’s silly to act like that’s the case. The website is just one piece of the sprawling and often bewildering film landscape.
As box office analyst Scott Mendelson wrote at Forbes:
For audience members who want to make good moviegoing decisions, the best approach is a two-pronged one. First, check Rotten Tomatoes and Metacritic to get a sense of critical consensus. But second, find a few critics — two or three will do — whose taste aligns with (or challenges) your own, and whose insights help you enjoy a movie even more. Read them and rely on them.
And know that it’s okay to form your own opinions, too. After all, in the bigger sense, everyone’s a critic.
Sourse: vox.com






