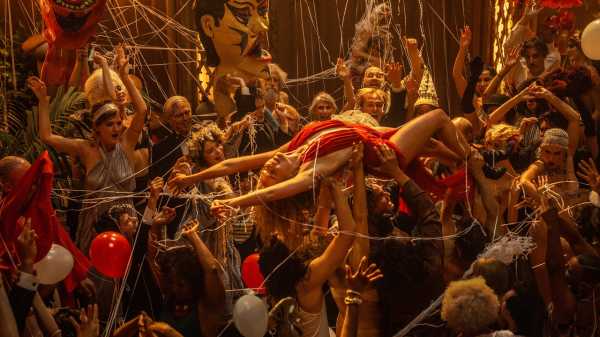
I’ve long suspected that the venom inspired by Damien Chazelle’s films is proportional to viewers’ devotion to their subjects—that his abuse of jazz in “Whiplash,” of acting and jazz in “La La Land,” and of history in “First Man” bothers most the people who care the most about those topics. His enthusiasts, meanwhile, exult in his way with myths—in his grandiose inflation of characters and their struggles into epic journeys. It’s as if, having felt the power of “Star Wars” through its incarnation of grand-scale myth, Chazelle applies its lessons to realistic quests and turns them into fantasies. He does it again in “Babylon,” which is set in Hollywood, mainly from 1926 to 1932, although it’s a little different from its predecessors. What distinguishes it from Chazelle’s other films, and what it shares with another recent film of swoony movie-love by a filmmaker of sentimental bombast—Steven Spielberg’s “The Fabelmans”—is the vigor of its storytelling. I think that the vigor of both films is rooted in the same source: knowledge. Just as Spielberg knows his own past, Chazelle knows Hollywood lore, and doubtless learned much more of it in the planning and the research. It’s the movie’s good anecdotes, rather than any dramatic arc, that make “Babylon” engaging, over the course of most of its three hours and nine minutes. It also takes such lore at face value, befitting the aura of legend that enhances both real-life incidents from classic Hollywood and its tall tales; these stories were born to be chazelled.
“Babylon” and “The Fabelmans,” along with Sam Mendes’s “Empire of Light,” make for a magic-of-the-movies trilogy that’s imbued with a halcyon retrospective glow—a nostalgic admiration for Hollywood’s past glories. Spielberg’s film is set in the fifties and early sixties, Mendes’s film in 1980-81, and both see movies of those eras as redemptive. It’s Chazelle’s film that’s, surprisingly, the most ambivalent; it’s noncommittal about Hollywood movies of the more distant era in which it’s set. Oddly enough, he appears to have little to say about them, a scant idea of what they were like and what made some of them great and others not. What the movie exalts, and what Chazelle appears to love, is the personalities—with all their flaws—who made Hollywood synonymous with its visionary boldness and blundering excesses, its blithe vulgarity and cavalier insensitivity, its vast spectrum of opportunity and ferocious maw of self-destruction.
“Babylon” is “Singin’ in the Rain” as a tragedy, albeit one that’s also filled with satirical comedy. (Its first scene sets the satirical tone, with a deluge of shit coming from the rear of an elephant being transported to a blowout Hollywood party.) Like Stanley Donen and Gene Kelly’s 1952 film, which is explicitly and implicitly referenced in Chazelle’s, “Babylon” tells the story of Hollywood’s transition from silent movies to talking pictures. It’s centered on three characters. The aspiring actress Nellie LaRoy (Margot Robbie) is cognate with the earlier film’s domineering, petulant, and voice-challenged silent-film diva Lina Lamont (who, in effect, gets a backstory here). A breezy yet earnest leading man, Jack Conrad (Brad Pitt), embodies the dark fate that would have awaited Gene Kelly’s Don Lockwood if he couldn’t sing and dance. The third protagonist, who is in effect the hyphen between the two, is a producer’s factotum, Manuel Torres (Diego Calva), who falls for Nellie the moment he sees her crash her car into a statue. He gets her into his boss’s wild party, where she gets noticed and cast in a small role that launches her. Manuel—or Manny, the nickname that she gives him—has been dreaming of a job on a set; at the party, Manny meets Jack, who takes a shine to him and gets him the desired in.
What’s redemptive about the movies, for Chazelle, isn’t so much the experience of viewing them but the benefits of making them. There’s no young Spielberg here, using a small camera to make Hollywood-inspired magic with whoever’s on hand; rather, there’s Manuel’s rapturous desire to be a part of something “bigger” than himself; there’s Nellie’s furious drive to escape from a hellish family life. (When a director asks Nellie, who’s playing a bit part, how she’s able to cry on cue, Nellie responds, “I just think of home.”) The brassy aspirant uninhibitedly expresses her reason for breaking into movies: “You don’t become a star, you either are one or you ain’t. I am.” As for Jack, he knows that he was a nobody before becoming a star, and he’s greatly devoted to making movies that connect deeply with “real people on the ground”; to do so, Jack wants the movies to be more innovative, audacious, and artistic. He says that he wants films to become as up to date and cutting-edge as twelve-tone music and Bauhaus architecture, “so that tomorrow’s lonely man can say, ‘Eureka, I am not alone.’ ” More plausibly, he likens the arrival of sound in movies to the discovery of perspective in painting.
Chazelle depicts the freewheeling anarchy of silent-film shoots: shouting, jousting, talking trash while the camera rolls, rowdy improvisation, last-minute derring-do. The movies made that way, he suggests, showed people as they really are, in contrast to the clinical, constrained solemnity and theatrical artifice of sound-stage work in the early days of talking pictures. The uninhibited boldness of Nellie’s earthy silent-film début and the sentimental heartiness of Jack’s silent-drama presence make a mockery of the silliness of Jack performing the song “Singin’ in the Rain” with a bouncy choral ensemble or the rigidity with which the untrained Nellie needs to hit her marks and deliver her lines in her first talking picture. (The latter scene, one of Chazelle’s many extended set pieces, borrows many of the elements from the mishaps of sound-filming depicted in “Singin’ in the Rain”—microphones in fixed positions, hidden amid décor, dictating actors’ placement and gestures and hampering their performance.)
The nasal-voiced, Joisey-accented Nellie apparently does little to develop (or even seek) the dose of theatrical skill needed to make the transition to sound; she’s too busy indulging in various forms of self-destructive frivolity. Manny rises quickly from unquestioningly intrepid assistant (breaking a strike, stealing an ambulance) to producer, but his devotion to the studio pushes him a step too far, as he betrays his principles and his friendships and comes to grief the melodramatic way, through moony swoony love. These unhinged personalities are just a few among many: the unprincipled yet discerning gossip columnist Elinor St. John (Jean Smart); the unlucky-in-love producer George Munn (Lukas Haas); the gifted, hard-edged female director Ruth Adler (Olivia Hamilton); the intertitle writer and lesbian artiste Lady Fay Zhu (Li Jun Li); the Black jazz musician Sidney Palmer (Jovan Adepo), whom Manny propels to stardom; the temperamental German director Otto von Strassberger (Spike Jonze); the drug dealer and aspiring actor called the Count (Rory Scovel); and the real-life “boy genius” producer Irving Thalberg himself (Max Minghella); plus a vast crew of hangers-on, acolytes, fixers, dreamers, and manipulators. They all form a wonderland, a magic kingdom that spews forth fictions that, however contrived or implausible, embody the realities of the passions, the risks, the devastations, the carnal pleasures, the obscene material splendors, and the ferocious drive to obtain them (along with at least a few drops, however diluted or adulterated, of sincere artistic ambition).
Chazelle’s vision of the myth-mad vitality and built-in tragedy of classic-era Hollywood comes at the price of its substance. The movie offers no politics, no history—1929 comes and goes with no stock-market crash (which in real life hit Hollywood and its players hard), no Depression, no electoral campaigns. There’s little sense of the corporate side of Hollywood, the hard-nosed boardroom management, the studios’ industrial organization (which is already on display in King Vidor’s inside-Hollywood comedy “Show People,” from 1928). These absences are more than merely factual; they set a tone for the movie that turns the tragedy superficial and the comedy decorative. Supernumeraries get killed and stories get silenced (except when they don’t), but there’s neither a sense of the mutual back-scratching or the power behind the suppression of news, no sense of the law at the studio gates, whether in threatened prosecutions or looming censorship—no Hays Code. Chazelle whips the story into cream-puff whorls of myths upon myths. He delivers a movie that’s neither unified nor disparate but homogenized, its elements of reality and hyperbole alike assimilated to the same creamy glow of rueful wonder. (The Coen brothers’ “Hail, Caesar!” has twice as much substance and vastly more humor—and compassion—at just over half the duration.)
Chazelle also puts forth a view of the magic of the movies in a phrase that strikes me as appallingly oblivious and unthinking, when Jack, facing newly hostile audiences, asks Elinor why he’s losing his appeal and she answers, “There is no why.” It’s approximately the line that Primo Levi relates regarding his internment in Auschwitz: he responded to a guard’s cruelty by asking why, and the guard responded, “Here there is no why.” I almost fell out of my seat.
“Singin’ in the Rain” offered a triumphalist point of view, asserting that the styles of the new, postwar Hollywood were indeed advances on the artifice and extreme stylization of silent movies and the primitive techniques of earlier talking pictures. It came amid a time of actual rapid artistic and cultural change in Hollywood: “Singin’ ” premièred just eleven years after “Citizen Kane,” four years after the court decision that helped to break up studio dominance and opened the door to independent producers, and during the rise of television, which thrust Hollywood into economic crisis. The self-satisfaction of “Singin’ in the Rain” had some aesthetic justification, but it also had a major thread of Hollywood self-advertising. “Babylon” is something of a work of salesmanship, too, offering a pitch for freestanding movies seen on the big screen at yet another moment when movie studios and theatres are facing economic disaster. Like “Singin’ in the Rain,” “Babylon” reaches from the past into the cinematic present, with another fact-based fantasy—a wild montage of subliminally brief clips that build the arc of movie history from Muybridge and the Lumière brothers to nineteen-sixties modernists and onward to recent cinematic times; it bends inevitably toward Chazelle. Artistically, what “Babylon” adds to the classic Hollywood that it celebrates is sex and nudity, drugs and violence, a more diverse cast, and a batch of kitchen-sink chaos that replaces the whys and wherefores of coherent thought with the exhortation to buy a ticket, cast one’s eyes up to the screen, and worship in the dark. ♦
Sourse: newyorker.com






