If all goes well, on Thursday at 3:55 pm ET, the planet Mars will have a new robot resident. That’s when NASA’s Perseverance rover is scheduled to touch down on the Red Planet, after its seven-month journey through space. You can watch NASA’s live broadcast of the landing below (starting at 2:15 pm ET).
Prepare to see some very tense-looking engineers around 3:48 pm. That’s when Perseverance enters its “seven minutes of terror” landing sequence. Because it takes several minutes for any communication from Mars to reach Earth, NASA’s team cannot pilot the rover’s landing. So Perseverance has to land itself, without any guidance from humans.
Why is this so terrifying? Simply: NASA won’t know if the rover has landed safely for those seven minutes — and the space agency doesn’t have a perfect track record when it comes to landing on Mars.
Previous rover missions were after one big question: Was Mars ever hospitable to life? They found that it was, with water once on the surface and organic chemicals in the environment.
Perseverance is going to go for the next big question: Is there evidence of actual microbial life, frozen in time on the Martian surface?
“This Mars mission is going to be the first mission to actually go and directly search for past evidence of life on Mars,” Philip Twu, a robotics engineer at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory who helped design Perseverance’s autonomous driving system, told me in July.
This is stuff scientists dream about answering as kids. And now, thanks to this latest mission, they have a good shot at it.
Meet Perseverance. It’s like NASA’s Curiosity Rover, but upgraded.
The Perseverance rover will look familiar to many.
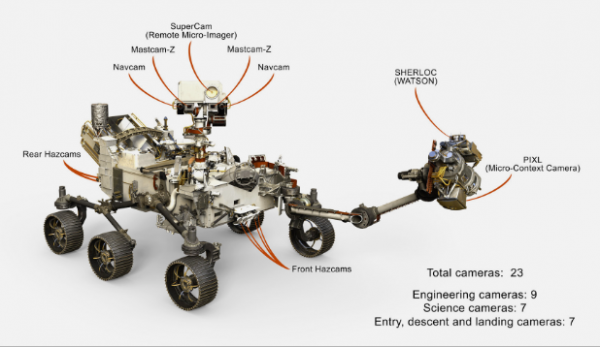
It’s modeled after the Curiosity, which landed on Mars in 2012. Like a new-model-year car, Perseverance comes with many upgrades: It can travel faster, farther, and around more obstacles on the Martian surface than Curiosity can. It has improved autonomous driving and more resilient wheels. It has a drone helicopter aboard (called Ingenuity), which will become the first of its kind to fly on another planet (this is more of a technology demonstration than a main mission tool).
It even has an experiment designed to generate oxygen from the Martian atmosphere, as a proof of concept for future rocket fuel factories on the planet.
And like any new piece of engineering these days, it comes with more cameras than the previous model: 23, compared to Curiosity’s 17.
But perhaps most important are the rover’s power tools: Perseverance is going to drill into an ancient river delta on Mars and collect rock samples that may contain evidence of ancient life. Even more audacious is the follow-up plan: A future mission will recover those samples from Mars and return them to Earth.
“Seven minutes of terror”
To find out the answer to that epic question — did Mars ever have life? — first, Perseverance will have to travel through space for seven months to reach the Red Planet.
Upon arrival to Mars Thursday, it will have to repeat an exceedingly tricky landing first achieved by Curiosity. The rover and all its gizmos are too heavy to land on the planet via parachutes alone. (Mars’s atmosphere is thinner than Earth’s to begin with, so parachutes are less effective there.) It has to be slowed downed with a powered (rocket) descent.
When Perseverance is just above the surface, the 2,260-pound rover will be lowered gently from the rocket via what NASA’s engineers call a “sky crane.”

This whole feat is made more impressive by the fact that Perseverance has to land itself. Mars is far enough away from Earth that any radio signal we send the rover takes seven minutes to reach Mars. That means there’s no piloting Perseverance in real time. It has to slow itself down from around 12,000 mph to zero, all while choosing an unobstructed place to land.
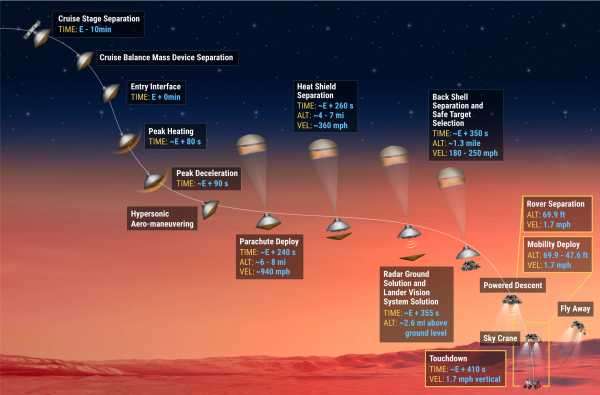
Even though Curiosity pulled off this feat in 2012, “our hearts will still be beating hard when we get to that point of the mission,” Matt Wallace, deputy project manager for Perseverance, told reporters before the mission launched. This is the most dangerous part of the whole mission, and the point at which it could fail catastrophically. Once the landing sequence starts, NASA will have no control over the craft.
Engineers call this landing the “seven minutes of terror” because we won’t find out if Perseverance has made it safely to the surface until it has landed and sent a radio transmission back to Earth. (Unlike Curiosity, Perseverance will be able to film its landing, which the public will be able to see at a later date. That will be rad.)
Looking for signs of ancient life
Curiosity landed in Gale Crater, a dried-up ancient lake bed. Perseverance is going to a location called Jezero Crater, which is an ancient river delta. The terrain there is a little more treacherous than Gale, but the rewards may be richer.
“It’s going to be a lot more rocks, it’s going to be a lot more cliffs, there’s going to be a lot more things that are going to really require a rover to be able to be a lot smarter in the way it drives,” Twu says. It all has to work perfectly: If the rover gets stuck or breaks a wheel, there’s no Martian equivalent of AAA to tow it.
As with any Mars mission, many technical malfunctions are possible. Last year, for instance, a heat probe on NASA’s Mars Insight lander got unexpectedly stuck while drilling into the ground.
But the risk will be worth it. “If life ever did exist on Mars, this is the kind of place where that evidence would be preserved,” Lori Glaze, the director of NASA’s planetary science division, told Vox in July.
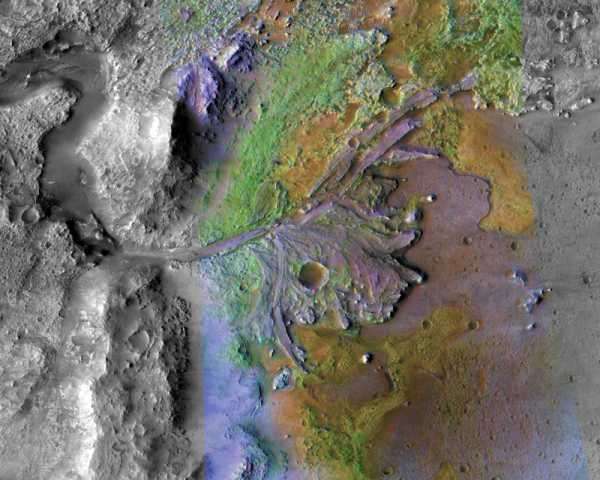

That’s because the crater is home to a 3.4 billion-year-old dried-up river delta. You can see its shape in the image above. This is an ideal place to look for signs of past life, Tanja Bosak, an MIT geobiologist working on the Perseverance mission, said.
In a river bed, “there are a lot of clay minerals, and as they settle, they can really just kind of smother anything organic, or they can even absorb organic molecules,” she says. That is: In the ancient dried clay of the delta, there may be microscopic fossils of microbial life, or geological patterns indicative of life. (Typically, Bosak studies how microorganisms alter rocks on Earth. The research she and her colleagues are doing in this area will provide the basis for what rocks to look out for on Mars.)
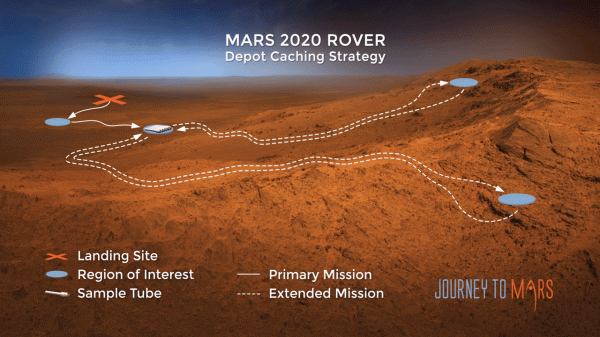

Once in the delta, Perseverance will use its cameras and various chemical sensors to find the rocks most likely to contain this evidence. (One of the sensors is called SHERLOC, short for “Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman & Luminescence for Organics & Chemicals.”) Scientists here on Earth will analyze that data and choose several dozen samples for the rover to drill into. Then the samples will be stored in special tubes inside the rover, where they’ll be undisturbed.
The most audacious plan, though, is to come. A future mission — whose date is not yet determined — called the Mars sample return will send a new rover to Mars to collect the samples from a drop-off point and then launch those back to Earth on a small rocket.
What type of life might scientists find?
Once back on Earth, scientists can study the samples extremely precisely and determine whether they contain signs of ancient life.
They’re not expecting anything more than microbes — bacteria-like, or other single-celled organisms. This is not a mission to find little green men.
But it still is exciting. “These [Martian] rocks are older, by half a billion or a billion years, than anything that’s well preserved that we have on Earth,” Bosak says. Which means we might not only find life on Mars but a form of life older and more primordial than any previously observed on Earth. When it comes to life on Earth, she says, we can’t even ask “what life was like on Earth at that time.” The potential evidence of life on Mars may give us a better understanding of how life evolved on our own planet.
Of course, the discovery of life on Mars will also provoke epic questions, like: Did life originate on Mars separately from Earth? Was there a common event that created life on both planets? Did life start on one planet and then jump to another via meteorite? Scientists won’t have these answers right away, but with actual samples from Mars, they can start thinking about them. (It’s also possible these Martian samples show no signs of ancient life.)
“Is there life in space?” is one of the biggest questions that gets kids interested in science. But scientists usually have to settle for figuring out the answers to smaller questions. “You learn to ask questions you can actually answer,” Bosak says. Now, in the relatively near future, we might be able to answer the big question.
“This is something that is so unashamedly cool,” Asad Aboobaker, an engineer who worked on an experimental oxygen generator aboard Perseverance, said in a July interview. This is his first Mars mission, and he’s just giddy about it. “Like, I get to send something to Mars, right? I mean, it’s literally going to go to another planet and land there, and it’s going to do something that’s never been done before.”
It’s something hopeful to think about during the coronavirus pandemic. The rover was named Perseverance in March after NASA conducted a nationwide essay-writing contest asking students for their ideas. Back then, the pandemic was not all-encompassing. Now the name has a new significance for many of the NASA engineers who have had to finish their work from home, or in person with increased biohazard safety burdens. “The name has taken on a lot of special meaning,” Glaze says. “The team has really had to overcome unbelievable obstacles.”
Help keep Vox free for all. Make a contribution today.
Sourse: vox.com