Doctors at NYU Langone in New York City announced Wednesday that they have successfully transplanted a genetically engineered pig kidney into a human who was declared brain dead, in what they called "a landmark step forward."
A surgical team removed the kidneys of the human recipient in July 2023 and transplanted the pig kidney, as well as the thymus. Before the transplant, the pig kidney was modified to remove alpha-gal, a sugar molecule on the surface of pig cells that triggers a rare allergy to red meat, as well as organ rejection.
Dr. Robert Montgomery, a professor and chair of the department of surgery at NYU Langone Health and director of the NYU Langone Transplant Institute, said the recipient's kidney has functioned properly for a month and that its function will be monitored for a total of two months.
MORE: 2 patients receive double-lung transplants due to rare 'flipped organs' condition
"The one-month kidney biopsies and kidney tests show no evidence of rejection, and normal renal function," Dr. Montgomery said during Wednesday's press conference. "The pig kidney appears to replace all of the important tasks that the human kidney manages."
Dr. Adam Griesemer, a transplant surgeon at NYU Langone Health, explained during the press conference that the thymus was also transplanted, embedded beneath the kidney's outer layer, because it has been shown to help protect the transplanted kidney from being attacked by the human immune system.

Maurice Miller, who was declared brain-dead, had a genetically-engineered pig kidney transplanted into him. His kidney function continued for a month and will be monitored for two months.Courtesy of The Miller Family
"The thymus gland is the tissue in our neck and chest where our immune system matures and where it learns to recognize the proteins in our body and learns to reject proteins that are not part of our own body," Dr. Griesemer explained. "So, transplanting the thymus from the pig allows new developing cells in the recipient's body to learn to recognize the pig antigens as their own, and it can potentially lead to a decreased immune response and decreased risk of rejection."
The transplant recipient was 57-year-old Maurice Miller. His sister, Mary Miller-Duff, expressed pride in her brother being involved in the historic transplant.
"Mo, as I like to call him, was a kind, giving brother who loved life, and always lent a helping hand," Miller-Duff said at the press conference. "It is only fitting that in his final act, he will be helping so many in the need through this innovative medical advancement."
Miller-Duff said her brother came home from work one day with a headache and feeling as if he had vertigo. His partner later found him passed out in the bathroom.
Scans revealed Miller had an eight-centimeter-wide tumor on the right side of his brain. Doctors performed a biopsy, but Miller didn't wake up after the procedure.
MORE: Family speaks out after man receives pig heart in 1st of kind transplant
"So, the doctors did a head scan and they found that there was bleeding on the brain and that's why he wasn't waking up," Miller-Duff said. "They went in to try to relieve that, but he just didn't wake up."
Tests revealed that the tumor was a glioblastoma, one of the most aggressive forms of brain cancer.
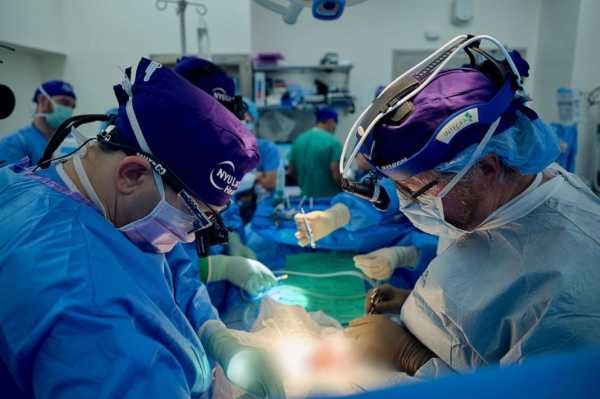
Dr. Jeffrey Stern, left, and Dr. Robert Montgomery prepare to implant a genetically engineered pig kidney into the recipient’s abdomen.Joe Carrotta/NYU Langone Health
The pig-to-human transplant is a hopeful sign that xenotransplantation – the process of transplanting non-human cells and organs into humans – may be viable after years of failures.
Last year, the University of Maryland School of Medicine transplanted a genetically modified pig heart into a 57-year-old man who was experiencing end-stage heart failure and did not qualify for a traditional transplant. Two months later, the organ failed suddenly, and the recipient passed away.
Dr. Montgomery said concerns about potential infection of the pig heart in the University of Maryland case, which may have contributed to the transplant's ultimate failure, was mitigated for the current transplant with a new test that he said "is much more sensitive at detecting viruses that aren't present in the blood that that are more difficult to detect."
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has not allowed living human xenotransplantation clinical trials due to the risk of transmission of viruses, but Montgomery said he hopes that fact that Miller has not developed any infections helps the agency reconsider their current policy.
In a separate procedure, a team at the University of Alabama at Birmingham published a study Wednesday that found two gene-edited pig kidneys functioned for seven days in a brain-dead recipient, compared to the 60 days in the NYU Langone recipient, while using "current standard-of-care immunosuppression drugs," according to the university.
Sourse: abcnews.go.com






