How industrial meat and dairy trap us in an infectious disease cycle.

Marina Bolotnikova is a deputy editor for Vox’s Future Perfect section. Before joining Vox, she reported on factory farming for national outlets including the Guardian, the Intercept, and elsewhere.
H5N1, or bird flu, has hit dairy farms — but the dairy industry doesn’t want us saying so.
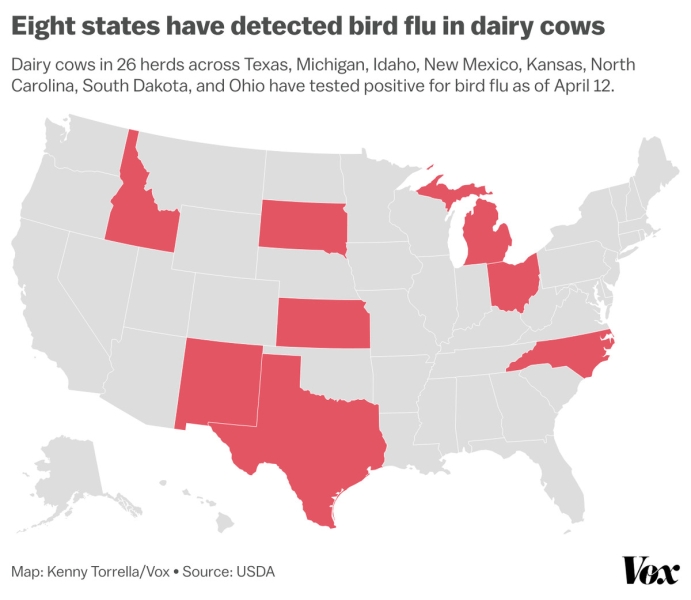
The current, highly virulent strain of avian flu had already been ripping through chicken and turkey farms over the past two years. Since it jumped to US dairy cows for the first time last month, it’s infected more than 20 dairy herds across eight states, raising alarms among public health authorities about possible spread to humans and potential impacts on the food supply.
One Texas dairy worker contracted a mild case of bird flu from one of the impacted farms — the second such case ever recorded in the US (though one of hundreds worldwide over the past two decades, most of them fatal).
Whatever fear-mongering you may have seen on social media, we are not on the cusp of a human bird flu pandemic; the chances of further human spread currently remain low. But that could change. As the virus jumps among new mammal species like cows, the risk that it’ll evolve to be able to spread between humans does increase.
But the American Association of Bovine Practitioners (AABP), an organization of beef and dairy veterinarians, declared in a statement (condemned by public health experts) last week that it doesn’t believe bird flu in cows should be considered bird flu at all.
“The AABP will call this disease Bovine Influenza A Virus (BIAV),” the association’s executive director K. Fred Gingrich II and president Michael Capel said in a statement, encouraging federal and state regulators to do the same. “It is important for the public to understand the difference to maintain confidence in the safety and accessibility of beef and dairy products for consumers.”
In other words, industry vets are trying to rebrand bird flu so that we keep calm and keep buying cheeseburgers. “They’re worried about selling products,” bovine veterinarian James Reynolds, a professor at Western University’s vet school, told me, calling the group’s statement “disease-washing.”
Covering bird flu over the last two years, I’ve seen a lot of wild stuff, but this may be one of the weirdest. And it’s more than just a terminological or political spat: It reflects an inescapable paradox about how we produce food.
The meat industry’s infectious disease trap
Naming infectious diseases is always political.
In this case, the cattle industry appears desperate to distance itself from the bird flu news cycle and avoid the perception that it’s contributing to human disease risk. But animal agriculture is one of the top drivers of zoonotic diseases — and growing global demand for meat, dairy, and eggs may be putting us at ever-greater risk of new outbreaks.
To understand why, one of the most elegant models I’ve found is the “infectious disease trap,” a concept coined in a 2022 paper by New York University environmental scientist Matthew Hayek.
Farming animals for food requires lots of land — much more land than it would take to grow an equivalent amount of plant-based foods. More than a third of the planet’s habitable land is devoted to animal agriculture alone, making it the world’s leading cause of deforestation as forests are cleared for farms. That in turn leads to more human and farm animal encounters with wild animals, a major source of new zoonotic diseases.
Animal agriculture’s land use can be shrunk through intensification — densely packing animals into factory farms — which limits deforestation and helps reduce meat’s climate footprint.
But such operations are terrible for animal welfare, and they exacerbate zoonotic disease risk in other ways, allowing viruses to rapidly tear through factory farms filled with thousands of stressed, genetically identical animals.
That’s exactly what’s been happening at chicken and turkey farms across the US over the last two years — and to prevent further spread, farmers have killed more than 85 million poultry birds on farms hit with bird flu since 2022, often using a grisly method that kills them via heatstroke. Our current food system is a recipe for brewing more virulent disease strains and, many experts fear, it’s a ticking time bomb for the next pandemic.
As long as global meat production expands, Hayek’s model explains, both low-density and factory farm-style animal agriculture trap us with rising disease risk.
What does this mean for the future of bird flu in cows?
A lot remains unknown about how bird flu has spread so rapidly among cows on dairy farms as far apart as Michigan and New Mexico.
One plausible theory is that the disease is moving with cows being trucked across the country, just as a human disease might move with people.
In recent years, as the dairy industry has increasingly consolidated into large factory farms, long-distance transportation of cows has become very common, Reynolds explained. Young female calves are often trucked from northern states to warmer climates in the south, then shipped back north when they’re old enough to become pregnant and produce milk. “There’s kind of a constant movement that really didn’t exist much 20 years ago,” Reynolds said.
Long-distance shipment can inflict extreme suffering on farmed animals, who are treated more like cargo than sentient beings. It’s also a hallmark of intensive animal agriculture systems described in the infectious disease trap model, allowing diseases to jump to new regions.
At least 18 states have restricted cow imports from states where dairy cows have tested positive for bird flu. The dairy industry recognizes the risks, Reynolds said, and is making efforts to improve biosecurity on these cross-country journeys. Meanwhile, regulators are scrambling to track the disease and stem its spread — but experts have argued those efforts don’t go nearly far enough, failing to require widespread testing.
And whatever steps are being taken now to stop the spread, the infectious disease trap model shows us that if we’re chasing zoonotic diseases after they’ve infected farm animals, we’re already behind.
Escaping that trap requires a much broader societal rethinking of our factory farm system.
This story appeared originally in Today, Explained, Vox’s flagship daily newsletter. Sign up here for future editions.
Source: vox.com