
Subscribe »
touchstones
Nirvana’s “Nevermind”
The 1991 album that gave rise to a rock genre and captured the spirit of a new generation.
Text by Hua Hsu



Supported by Tiffany & Co.

“Touchstones” is an ongoing digital series in which New Yorker writers guide us through their favorite works of art.
In the late eighties, a small community of talented, sludgy local bands began attracting attention in the Pacific Northwest. Few had realistic ambitions of mainstream success, devoting themselves instead to an underground economy of independent record labels and loud, albeit small, gigs.
The Seattle Scene
The underground music scene in and around Seattle—later dubbed the birthplace of grunge—was made up of punk- and heavy-metal-influenced bands that didn’t aspire to commercial success.


“Touch Me I’m Sick”
Mudhoney
(1988)


“Start at the Top”
Skin Yard
(1989)


“Gila”
The U-Men
(1984)


“Saddle Tramp”
Dickless
(1990)


“Flower”
Soundgarden
(1988)
One of those bands was from Aberdeen, Washington, just outside Seattle, and called itself Nirvana: a sunny, hippy-ish reference to a stage of Buddhist enlightenment. Despite its joke of a name, the group played music that was heavy and deafening—because if failure seemed a foregone conclusion, why not at least have fun?
Nirvana’s sense of playful irony, which you could hear in its music, set the band apart from many of its doom-and-gloom peers in what would become known as the Seattle scene. In 1989, Nirvana signed to Seattle’s Sub Pop Records and released its first studio album, “Bleach.”

Nirvana performing “School,” from “Bleach,” in Denver, in 1989.
Nirvana had a reputation for writing surprisingly catchy songs and for putting on chaotic live shows, such as the band’s performance in Denver on the “Bleach” tour. These shows revolved around its charismatic lead singer and guitarist, Kurt Cobain. He had presence. In the eyes of major-label executives, perhaps he could even be positioned as a new kind of anti-rock star.

Slash in the Guns N’ Roses video for “November Rain,” 1991.
At the time, I knew none of this. I was just a teen-ager in Cupertino, California, turning the dial, looking for something different. Back then, the divide between mainstream and alternative music—a designation that had only recently emerged—still seemed meaningful. My local rock station was dominated by bands like Guns N’ Roses, Skid Row, and Van Halen, which were indebted to a hard, heavy, and theatrical style, full of big guitar solos and even bigger hair.

Slash in the Guns N’ Roses video for “November Rain,” 1991.
Mainstream rock seemed to fit within a limited gradient of American machismo, from fun-loving buffoonery to the serious and virtuosic. This isn’t to say that there were no other options: college radio had fuelled the rise of U2, Depeche Mode, and R.E.M., and punk had seeded small, intrepid, alternative scenes in places like Boston, Minnesota’s Twin Cities, and Athens, Georgia. But from my perch in suburban California those other options were still a challenge to find. And it seemed self-evident that musicians who rejected mainstream professionalism would remain on the fringes.
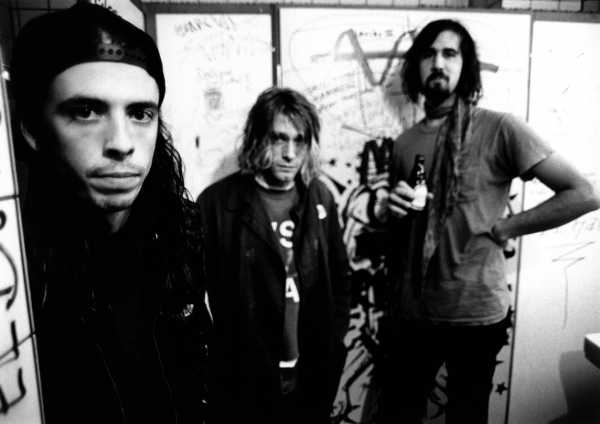

Nirvana in 1991. From left to right: Dave Grohl, Kurt Cobain, and Krist Novoselic.
There was a romance to pledging allegiance to these lost causes and underground voices. When Nirvana released its second album, “Nevermind,” in the fall of 1991, everything changed—for me, and for the pop-music ecosystem. The band, which now consisted of Cobain, the bassist Krist Novoselic, and the drummer Dave Grohl, had signed with a major label, Geffen Records. A few years earlier, Geffen had begun wagering that “alternative rock”—a category that began appearing on the Billboard charts around that time—could be a profitable niche. The label had signed Sonic Youth, respected pioneers of New York’s avant-garde rock scene, and a band whose trajectory and choices Cobain admired. Perhaps there was a strange excitement to smuggling something unusual into the mainstream. The cover of “Nevermind,” which featured a naked baby swimming toward a dollar bill, seemed a sly and hilarious allusion to signing with Geffen.
Nirvana’s first album, “Bleach,” had been produced for just six hundred dollars, and it more or less sounded like it: muffled, dingy, like early-draft Beatles songs swallowed in noise. “Nevermind” cost much more, and there was a lot more oversight. Like “Bleach,” it featured songs that alternated between bludgeoning, distorted guitars and sweet, catchy melodies. But the new album was prettier and more dynamic, powered by Grohl’s end-of-days drumming and Novoselic’s friendly, loping bass lines. There was more space for Cobain to sing and croon, not just shout—though he did that, too.
Nirvana’s Evolution
Compare the melodic “Lithium,” from Nirvana’s second album, to the heavy, muffled sound of “Floyd the Barber,” from the band’s début album.

“Floyd the Barber,” from “Bleach.”

“Lithium,” from “Nevermind.”

Drag left and right to compare “Bleach” and “Nevermind.”
The perfect distillation of Nirvana’s newly refined sound was “Smells Like Teen Spirit,” which Cobain later described as his jokey attempt to write “the ultimate pop song.” On September 29, 1991, the music video for “Smells Like Teen Spirit” premièred on MTV’s late-night alternative-music show, “120 Minutes.” The video quickly went from the “120 Minutes” niche to the “Buzz Bin”—MTV’s showcase for up-and-coming bands—to constant rotation.

“Smells Like Teen Spirit,” from “Nevermind.”
I first heard “Smells Like Teen Spirit” that fall, on the local modern-rock station. I soon decided I needed to be able to hear to it whenever I wanted, so I bought the cassette of “Nevermind” as soon as it came out. I remember staring at my tape deck as I listened to it for the first time, overwhelmed by how many good songs there were. Nirvana would soon be the biggest band in America, but, in that moment, to a teen-ager casting about for something new, it still felt like a secret.
The Ultimate Pop Song
Cobain admired how The Pixies could move from “soft and quiet” to “loud and hard.” You can hear a similar dynamism in the opening of Nirvana’s “Smells Like Teen Spirit,” in which Cobain’s low-key guitar suddenly gives way to Grohl’s end-of-days drumming.
dist. guitar
clean guitar
bass
crash
hi-hat
snare
kick



































































































I became invested in the band’s identity as underdogs. As Nirvana became more popular, I remember how strange it was to hear it on drive-time radio, or see the band on MTV during the daytime. I even heard it on the local hip-hop station. Unlike the bands topping the mainstream rock charts, an assembly line of men with enormous, wavy hair and tight leather pants, Nirvana seemed young and spontaneous. Its members looked different from those other rock stars, too. It was much easier to dress like them.
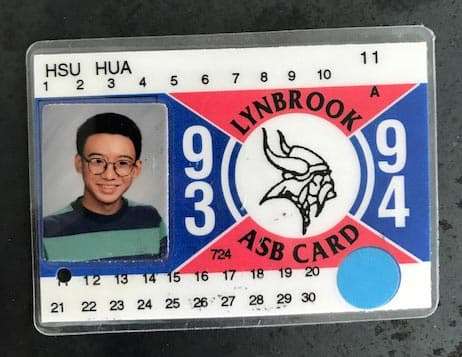
The author at age sixteen, sporting a T-shirt inspired by Cobain in the “Smells Like Teen Spirit” video.
Nobody—not Nirvana’s label, its management, or the band itself—was prepared for the velocity of its ascent. In January of 1992, “Nevermind,” which had débuted modestly, at No. 144 on the Billboard album chart, took over the No. 1 spot (displacing Michael Jackson’s “Dangerous”). The album would eventually go diamond, selling more than ten million copies in the U.S. alone.
It was exciting to see something so unexpected take off like that. For my friends and me, Nirvana’s unglamorous, D.I.Y. style was a welcome reaction against the groupie-chasing, hard-partying posing that had dominated MTV for so long. Nirvana was like an intruder in the temple, making those bands seem barbaric, and instantly irrelevant. But Nirvana was also tapping into something bigger: an emergent, far-flung world of youth culture that was proudly, at times self-consciously, “alternative.” A new spectrum of identities and creative forms seemed to infiltrate the mainstream, and the possibilities felt thrilling.
Alternative Nation
Nirvana tapped into an early-nineties youth culture that embraced new and multicultural identities, on display everywhere from feminist zines to reality TV, teen dramas, and independent films.

The cover of a Riot Grrrl zine.

The cast of the first season of “The Real World.”

“My So Called Life.”

“Slacker.”
The success of Nirvana and other Seattle bands, including Pearl Jam, Soundgarden, and Alice in Chains, changed the music industry. The breakout rise of “Nevermind” suggested that so-called alternative bands and niches could be commercially viable—not just as steady, low-risk earners but as the proverbial next big thing. Major labels began showering loads of money on tiny, Nirvana-esque bands that played a similar kind of “grunge” rock. The “grunge gold rush,” as the journalist Steve Knopper termed it, created boom-or-bust trajectories for bands that might have once settled for modest regional fame. It was no longer hard to find alternative sounds; major labels were desperate to pitch everyone as the next Nirvana.
The members of Nirvana acted nonchalant, sometimes even hostile, toward their fame. It didn’t help that they were becoming celebrities just when advertisers and cultural critics were trying to figure out how to label and define my generation. Cobain started to be called the voice of Generation X, and his resistance to the tag merely entrenched it further. Nirvana’s ambivalence came to be held up as a Gen X trademark; the band’s iconoclasm turned the musicians into icons.

Nirvana on the cover of Rolling Stone, 1992.
Cobain used his platform admirably, to promote underground bands from America and abroad. In interviews and liner notes, he stuck to his principles, and decried the casual sexism, racism, and homophobia of American culture.
“If any of you in any way hate homosexuals, people of different color, or women, please do this one favor for us—leave us the fuck alone! Don’t come to our shows and don’t buy our records.”—Kurt Cobain
“Incesticide” liner notes, 1992.
But the non-stop touring and celebrity took a huge toll on Cobain’s health and stability, and his heroin addiction, for which he had previously been in rehab, got worse. I wasn’t shocked when he took his own life, in 1994. There were rumors of overdoses and near-death experiences in the preceding months. But it was still jarring.
After his death, there were articles and nightly-news segments about Cobain’s nihilism, and what his choice suggested about the younger generation. Mostly, I remember listening to “Nevermind” over and over—not as a search for clues (for that, you’d listen to Nirvana’s last studio album, “In Utero,” and its many references to despair and illness), but as a reminder of how unlikely his trajectory had been. It was the first time I’d wondered how you could work both inside and outside the system—whether you could be critical of, say, the corporations underwriting your art while making art that aspired for worlds beyond those realities.
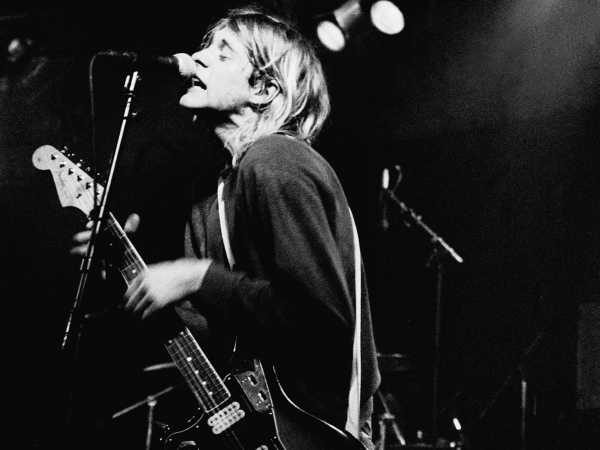

Cobain performing in Amsterdam, 1991.
At the time, I thought a lot about whether Cobain was actually “cool” and disaffected, or whether his coolness merely masked a deeper earnestness. Now I see that both things were true. People gravitated toward his persona because it didn’t seem like one; he seemed authentic. But, of course, it was a persona—just a more thoughtful, conflicted, and unguarded one than we were used to seeing.
There’s a sort of bittersweet aftermath to this story. “Nevermind” has since been absorbed into the rock canon. Just as kids a couple of years younger and older than me at school had wildly different opinions about whether Cobain was a saint or a sellout, every generation has their own version of the Nirvana legend. Nowadays, Cobain has become a fashionable reference point for musicians across genres, from pop to hip-hop, who want their music to seem brooding and emotional. Dr. Dre and Jay-Z today express admiration for the cultural rebellion that Cobain represented, describing his music as powerful enough to have briefly “stopped” hip-hop’s ascendancy.
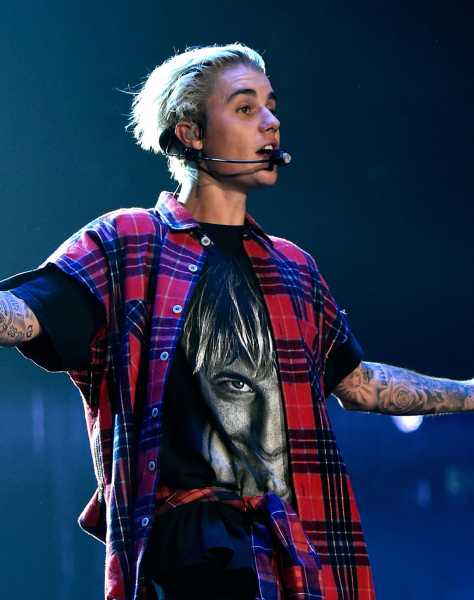

Justin Bieber.
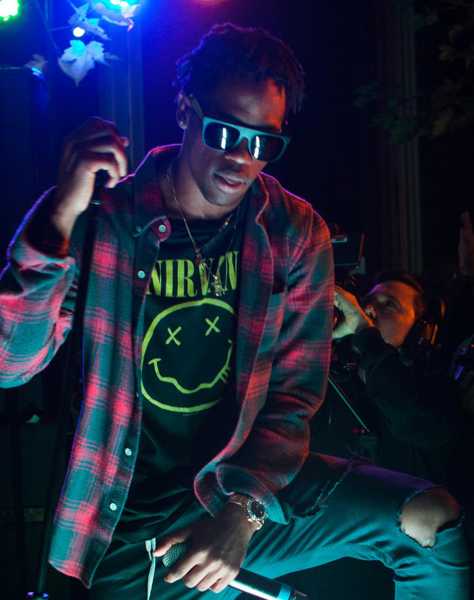

Travis Scott.
Maybe that’s the paradox of alternative culture that’s always been true, only it was our turn to realize it: pop culture is born anew each time an outlaw is discovered. Your pose lives on, even if the seeds of your own rebellion are forgotten.
Nirvana has become canonized as a gritty, punkish pop band working through a surplus of emotions, but I often think back to how radical the band was in its time: Cobain’s softness, his rejection of mainstream America’s self-serious machismo, Nirvana’s profound unease about being rock stars. The band was a gateway.
The Nirvana Gateway
Cobain used his platform to champion lesser-known artists and musicians from America and abroad.
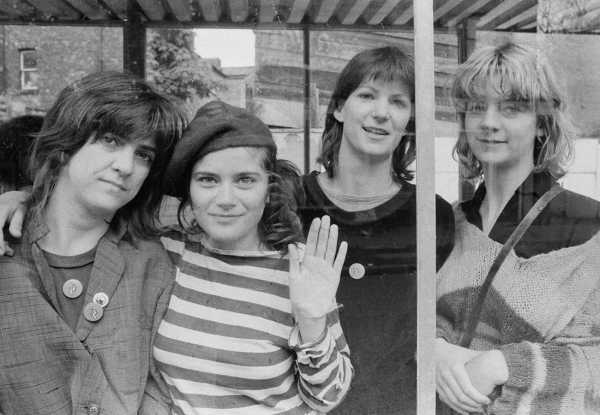

The Raincoats in 1979. “If it weren’t for the luxury of putting that scratchy copy of the Raincoats’ first record,” Cobain wrote, “I would have had very few moments of peace.”
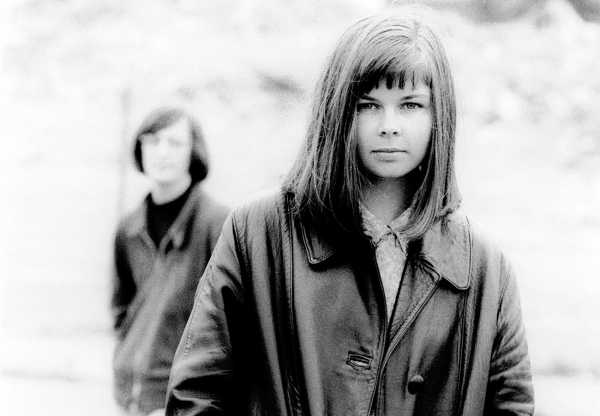

Cobain once called the Vaselines, pictured here in 1987, his “favorite songwriters in the whole world.”
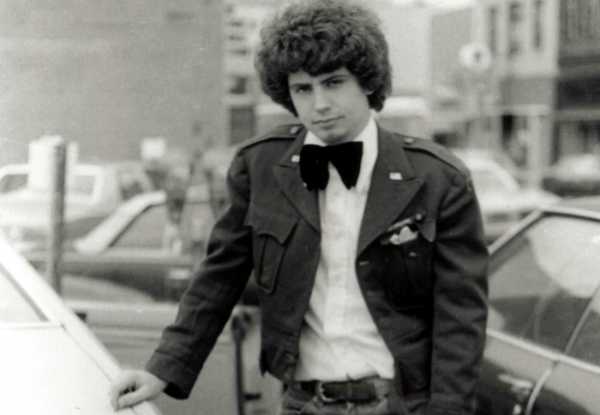

Daniel Johnston at age eighteen. Cobain often wore a T-shirt with artwork from Johnston’s “Hi, How Are You” album.
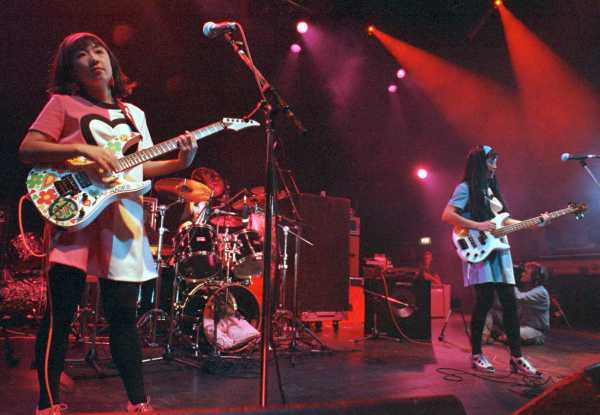

Shonen Knife in 1993. After seeing them play in L.A. in 1991, Cobain gushed, “I turned into a nine-year-old girl at a Beatles concert. I was crying and jumping up and down and tearing my hair out—it was amazing.”
My friends and I would hunt down obscure books, movies, and bands that Cobain championed, to try and figure out how he had come to be. Only we would never know. We followed Nirvana into new worlds of possibility, people brought together by songs describing one man’s private, unknowable despair.
Credits: Illustration by Bráulio Amado; Source Photograph by Jan Boeve / Hollandse Hoogte / Redux; Everett. The Seattle Scene: Sub Pop, Sub Pop, Big Bad Music / Bomb Shelter, Sub Pop, SST. Universal Music Group, 1991. Paul Bergen / Redferns / Getty. Nirvana’s Evolution: Universal Music Group, Sub Pop. The Ultimate Pop Song: Sub Pop. Hua Hsu. Alternative Nation: Mimi Nguyen, MTV / Everett, ABC / Everett, Orion Pictures / Everett. Mark Seliger / Rolling Stone. Peter Pakvis / Redferns. Kevin Mazur / WireImage / Getty. Roger Kisby / Getty. The Nirvana Gateway: Kevin Cummins / Getty, Alastaire Indge / Camera Press / Redux, “The Devil and Daniel Johnston,” directed by Jeff Feuerzeig, 2005, Anthony Pidgeon / Redferns / Getty.
More from the Touchstones series

Janet Jackson’s “Rhythm Nation 1814”
The album preached the unifying power of dance, and taught me that performance could be its own kind of genius.

Missy Elliott’s “Supa Dupa Fly”
The 1997 album that defined a new Hip-hop aesthetic and expanded the definition of rap.
Sourse: newyorker.com






