Researchers at the National Research University of Electronic Technology (MIET) have developed a new approach to organ regeneration, which is unmatched in terms of price and efficiency. According to the authors, the material they created will allow heart tissue to be restored after a myocardial infarction (heart attack), in just 2-4 months.
The results of the study were published in “Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy”, a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal.
According to MIET researchers, they were the first in the world to find a way to chemically bind carbon nanotubes to the molecules of the most common blood protein – albumin. The physical mechanism they discovered made it possible to develop a new method of using 3D laser printing to create nanocomposites.

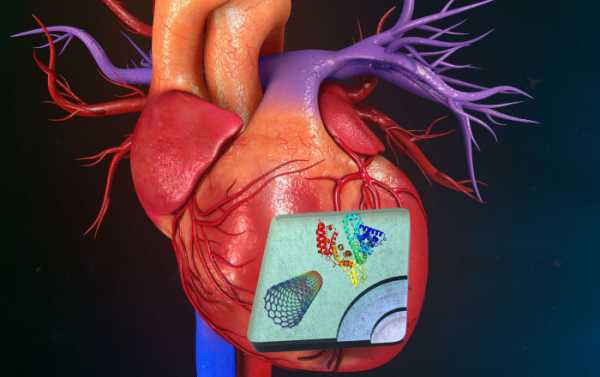
Diagram of a nanocomposite design for heart myocardial infarction
As the scientists clarified, they have created heart implants 3-4 times cheaper than ordinary Russian ones and 6-8 times cheaper than their foreign counterparts, exceeding both in a number of parameters. The technology is suitable not only for scaffolds used in tissue engineering but also for the production of biosensors, microfluidic systems and even advanced medications against cancer.

Layers of the nanocomposite structure created by covalent bonding of single-walled carbon nanotubes and albumin molecules
Before implantation, the printed scaffold is inhabited by live cells and “matures” for a while. As MIET National Research University specialists noted, several successful experiments have shown that stem cells capable of transforming into the cells of the tissue into which they were transplanted can also be used for this purpose.
The researchers are confident their method will effectively combat pathologies such as congenital heart disease and myocardial infarction, aneurysm, atherosclerosis and cardiosclerosis. According to them, a nanocomposite patch for myocardial infarction in 2-4 months completely regenerates the affected area, with the scaffold being dissolved.

The diagram of the formation of nanocomposite structures by laser printing and the image of a monolayer of cells of a connective biological tissue on a nanocomposite structure
The scientists noted that the technology has been developed in close cooperation with leading Russian scientific and technical centres. In the future, the team intends to move to the implementation of the method in clinical practice, as well as to adapt the technology to create coatings for various implantable systems.
Sourse: sputniknews.com






